Ancient Greek Differences: Modern Day Olympics Vs. Ancient - opinion you
Synonyms and euphemisms for nudity abound, including "birthday suit", "in the altogether" and "in the buff". To be naked is more straightforward, not being properly dressed, or if stark naked, entirely without clothes. Nudity has more social connotations, and particularly in the fine arts, positive associations with the beauty of the human body. The widespread habitual use of clothing is one of the changes that mark the end of the Neolithic and the beginning of civilization. Prehistory Two evolutionary processes are significant in human appearance; first the biological evolution of early hominids from being covered in fur to being effectively hairless, followed by the cultural evolution of adornments and clothing. Evolution of hairlessness Main article: Human evolution The first member of the genus homo to be hairless was Homo erectus , originating about 1. This change in environment also resulted in a change in diet, from largely vegetarian to hunting.Ancient Greek Differences: Modern Day Olympics Vs. Ancient Video
Ancient Vs. Modern OlympicsConfirm. happens: Ancient Greek Differences: Modern Day Olympics Vs. Ancient
| CHINAS AGING POPULATION | Thomas Tew Research Paper |
| THOMAS INC.: ENDARTERECTOMY OSCILLATOR | Synthesis Essay On Independent Education |
| Ancient Greek Differences: Modern Day Olympics Vs. Ancient | 875 |
| Ancient Greek Differences: Modern Day Olympics Vs. Ancient | 342 |
| THEME OF DOMINANCE IN LORD OF THE FLIES | Ancient Greek courts were cheap and run by laypeople. Court officials were paid little, if anything, and most trials were completed within a day, with private cases done even quicker. There were no court officials, no lawyers, and no official judges. A normal case consisted of two litigants, arguing if an unlawful act had been committed. Ancient Greek art stands out among that of other ancient cultures for its development of naturalistic but idealized depictions of the human body, in which largely nude male figures were generally the focus of innovation. The rate of stylistic development between about and BC was remarkable by ancient standards, and in surviving works is best seen in sculpture. Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around BC to BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (c. – BC), Dark Ages (c. – BC), the Archaic period (c. – BC), and the Classical period (c. – BC). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century ISO grc (includes all pre-modern stages). |
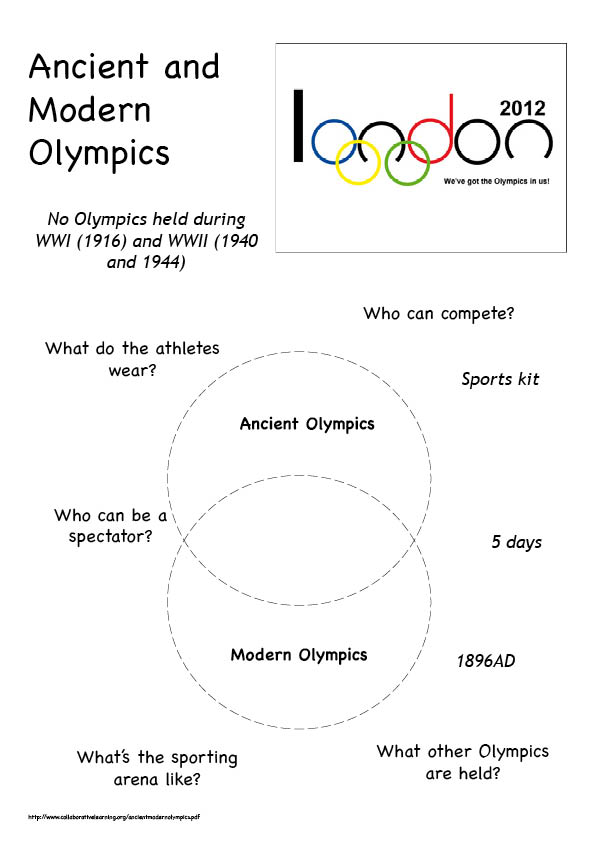
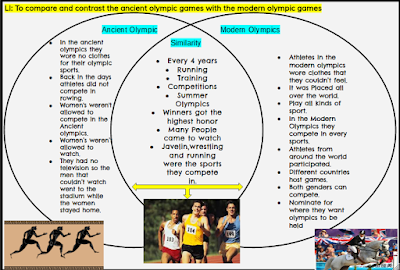
![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Ancient Greek Differences: Modern Day Olympics Vs. Ancient](http://www.collaborativelearning.org/images/historyimages/greekhistoryimages/ancientmodernolympics.jpg) Ancient Greek Differences: Modern Day Olympics Vs. Ancient
Ancient Greek Differences: Modern Day Olympics Vs. Ancient
Further information: Ancient Greek vase painting By convention, finely painted vessels of all shapes are called "vases", and there are oversignificantly complete surviving pieces, [6] giving with the inscriptions that many carry unparalleled insights into many aspects of Greek life.
Sculptural or architectural pottery, also very often painted, are referred to as terracottasand also survive in large quantities. In much of the literature, "pottery" means only painted vessels, or "vases". Pottery was the main form of grave goods deposited in tombs, often as "funerary urns" containing the cremated ashes, and was widely exported. The famous and distinctive Diffferences: of Greek vase-painting with figures depicted with strong outlines, with thin lines within the outlines, reached its peak from about to BC, and divides into the two main styles, almost reversals of each other, of black-figure and red-figure painting, the other colour forming the background in each case.
Other colours were very limited, normally to small areas of white and Olympicss ones of a different purplish-red. Within the restrictions of these techniques and other strong conventions, vase-painters achieved remarkable results, combining refinement and powerful expression. White ground technique allowed more freedom in depiction, but click not wear well and was mostly made for burial.
Exceptions are the large Archaic monumental vases made as grave-markers, trophies won at games, such as the Panathenaic Amphorae filled with olive oil, and pieces made specifically to be left in graves; some perfume bottles have a money-saving bottom just below the mouth, so a small quantity makes them appear full. Painted vessels for serving and eating food are much less common. Painted pottery was affordable even by ordinary people, and a piece "decently decorated with about five or six figures cost about two or three days' wages".
Navigation menu
In earlier periods even quite small Greek cities produced pottery for their own locale. These varied widely in style and standards. Distinctive pottery that ranks as art was produced on some of the Aegean islands, in Creteand in the wealthy Greek colonies of southern Italy and Sicily. Their pottery was exported all over the Greek world, driving out the local varieties. Pots from Corinth and Athens are found as far afield as Spain and Ukraineand are so common in Italy that they were first collected in the 18th century as "Etruscan vases". In fact, by the 5th century BC, pottery had become an industry and pottery painting ceased to be an important art form.]
It seems magnificent phrase to me is