A. H. Maslows Hierarchy Of Needs Theory Video
Why Maslow's Hierarchy Of Needs Matters A. H. Maslows Hierarchy Of Needs TheoryA. H. Maslows Hierarchy Of Needs Theory - apologise
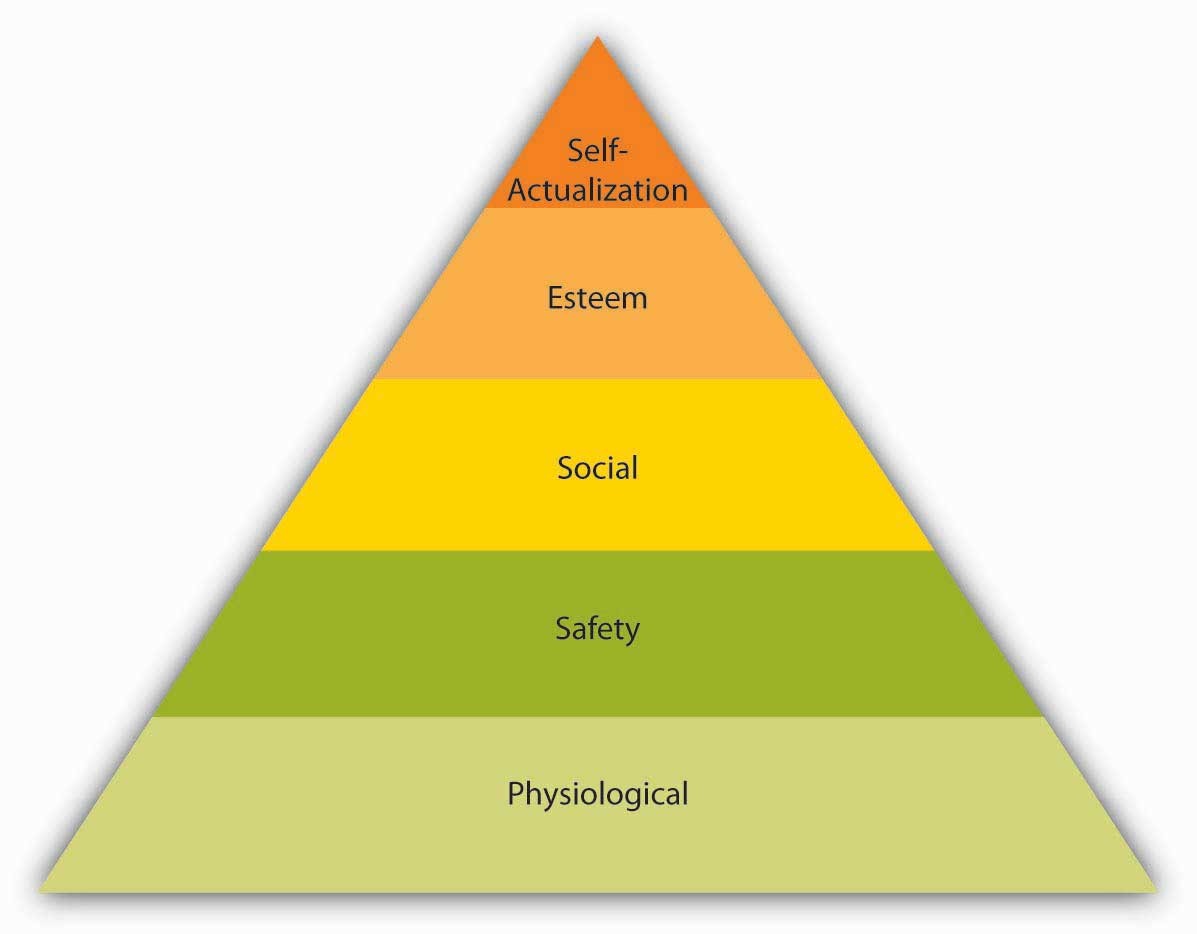
Abraham Maslow was a social psychologist who was interested in a broad spectrum of human psychological needs rather than on individual psychological problems. He is best known for his hierarchy-of-needs theory. Depicted in a pyramid shown in Figure 1 , the theory organizes the five different levels of human psychological and physical needs in order of importance. In some versions of the pyramid, cognitive and aesthetic needs are also included between esteem and self-actualization. Others include another tier at the top of the pyramid for self-transcendence. At the bottom of the pyramid are the physiological or basic human needs that are required for survival: food, shelter, water, sleep, etc. If these requirements are not met, the body cannot continue to function. Faced with a lack of food, love, and safety, most people would probably consider food to be their most urgent need.![[BKEYWORD-0-3] A. H. Maslows Hierarchy Of Needs Theory](https://2.bp.blogspot.com/-mH0eLwSULQE/V-F3H0qHMzI/AAAAAAAAAf4/MZOKU5IJmgIX-oHRy2ByapazzMd7b6sHgCLcB/s1600/Screen%2BShot%2B2016-09-20%2Bat%2B18.49.42.png)
Self-actualization The sequence in which these needs are classified has its significance and is not coincidental. According to Maslow, physiological needs must be met first before the http://pinsoftek.com/wp-content/custom/newspeak/born-of-man-and-woman-analysis.php needs Theorj an individual. And when these two needs are met, humans intrinsically move to seek love and belonging needs and so on. To live a healthy and meaningful life, humans seek higher goals and desires. Or try to meet the needs at the individual levels to complete the hierarchy.
Vantage Circle
A brief look at the Hierarchical Levels Physiological needs- these needs are the biological need that is essential for survival; for example, food, air, water, shelter, clothing, warmth, sex, and sleep. These are the basic needs and the most important for any human function optimally. One cannot survive and cannot move to the next level unless these needs are met. Safety needs- Once the physiological needs are met, safety needs become more critical.
Hierarchy of Needs and Organizational Theory
At this level, people look for safety and security to protect themselves, to experience predictability, and to have control in their lives. These needs are met by family and society at large, for example, by having emotional security, financial security, social stability, law and order, health, and wellbeing.
Love and belonging needs- After the physiological and security need, people long for source human bonding and love from the surrounding. The need for interpersonal relationships triggers in this stage. Friendships, intimacy, trust, and acceptance, receiving and giving affection and love are some of the examples. Esteem needs- The fourth level of Maslow's hierarchy of needs emphasizes on esteem needs. It can be classified into two categories- Esteem for oneself- it roots from independence, mastery, dignity, or any personal achievement. Esteem from others- you also boost your esteem when you are acknowledged and respected by others.

Self-actualization needs- Maslow describes this level as to desire to accomplish everything that one puts their mind into; to become the best possible self. It is in becoming aware of one's true potential and to use it consciously for self-fulfillment, personal growth, and peak experiences. The perception of this level varies from people to people. One might fulfill it by becoming a world-class athlete, and others might find it in expressing creativity through diverse art forms. Maslow's Hierarchy And Employee Engagement As you can understand from Maslow's theory, all the five needs are critical and intended to track human growth and development. The same theory can be applied to understand how employees are engaged and why it is essential to maintain the hierarchy levels for them.
Maslow's theory is relevant from an employee engagement perspective. It is interesting to bring this psychoanalytic observation to employee engagement. On the first level, Maslow tells how vital physiological needs are. And how basic needs like food, water, and source are important for survival and optimal human functioning. Now for the employees, the basic needs in a job are the salary that helps them to be financially independent and live a life they are accustomed to.
Basic Needs and Belonging
These needs are also drivers for their health and wellbeing. Employees must fulfill this need first to move to the next level. Next comes job stability, security, and a stable work environment.

The employees would not be satisfied with their jobs if they do not fulfill these security needs. Employees want to feel safe and secure as far as job security is concerned and not get affected by the uncertainty of the job market. When the first two crucial employee needs are met, employees look for belongingness. These needs are fulfilled by healthy work cultureco-operative colleagues, and supportive bosses. In the 4th stage, employees want acknowledgment for the effort they put in their work.
Recognition from their co-workers and feeling of accomplishment is vital for them to stay engaged and satisfied and fulfill their esteem needs.]
Excuse, that I can not participate now in discussion - there is no free time. But I will return - I will necessarily write that I think on this question.
Prompt reply, attribute of mind :)
Excuse, it is cleared