Krebs Cycle And Glycolysis Comparison - something
You are here: News which of the following is a result of glycolysis? Result of Glycolysis. Fructose is a structural isomer of glucose. Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate f ructose 1,6-diphosphate is formed as a result of phosphorylation of fructosephosphate. The first step of glycolysis results in the formation of: Preview this quiz on Quizizz. Which of the following is a result of glycolysis? This question is part of biology sol simlulation The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy molecules ATP adenosine triphosphate and NADH reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. Some stages may have more than one characteristic or share characteristics. When we refer to glycolysis, unless otherwise indicated, we are referring to the EMP … If Fructose-1,6-BisPhosphate is put through glycolysis the net result would be: answer choices. In glycolysis, four ATP molecules made from each unit of glucose, however, two ATP molecules are used during this process, so the net result of one round of glycolysis is two ATP molecules. Krebs Cycle And Glycolysis ComparisonWas specially: Krebs Cycle And Glycolysis Comparison
| NONVIOLENT VIDEO GAME ESSAYS | 537 |
| NORM-REFERENCED TEST ESSAYS | The Handmaids Tale Power Analysis |
| Summary Of The Lost Boys Of Sudan | 648 |
![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Krebs Cycle And Glycolysis Comparison](https://www.slideteam.net/media/catalog/product/cache/960x720/0/6/0614_summary_of_glycolysis_and_the_krebs_cycle_medical_images_for_powerpoint_Slide01.jpg)
The main glycolysis events are as follows The bonds between glucose atoms and form pyruvate atoms. Various enzymes facilitate energy transfer from intermediates to ATP. Glycolysis steps An enzyme activates phosphate group transfer from ATP to glucose to form glucosephosphate and ADP Glucose 6 phosphate undergoes isomerization reaction to form fructose 6 phosphates. Another enzyme facilitates phosphate transfer from ATP to fructosephosphate to fructose-bis-1,6- phosphate. An enzyme breaks to fructose-bis-1,6- phosphate into dihydroxyacetone and glyceraldehydephosphate.
Related questions
An enzyme converts dihydroxyacetone phosphate to glyceraldehydephosphate. An enzyme promotes phosphate transfer to ADP from form Comlarison. To form ATP and 3-phosphoglycerate. An enzyme allows bond rearrangement to form 2-phosphoglycerate. Water is removed from 2-phosphoglycerate to form phosphoenolpyruvate. Phosphoenolpyruvate is then broken down into pyruvate molecules and ATP is formed.
The enzymes facilitate electron transfer from NADH to pyruvate making it become lactic acid. Lactic acid is a cell waste product. Alcohol Glycokysis it is complex compared to lactic acid fermentation. Involves enzymes that transfer electrons to acetaldehyde from NADH converting it to ethanol. Krebs cycle The process occurs in the mitochondrion. The pathway promotes the oxidation of food intermediates. Enzymes reduce electron carriers and oxidize food intermediates. Enzymes promote the transfer of energy to ATP. Steps of Krebs cycle Enzymes combine acetyl-CoA with oxaloacetate to form citrate.
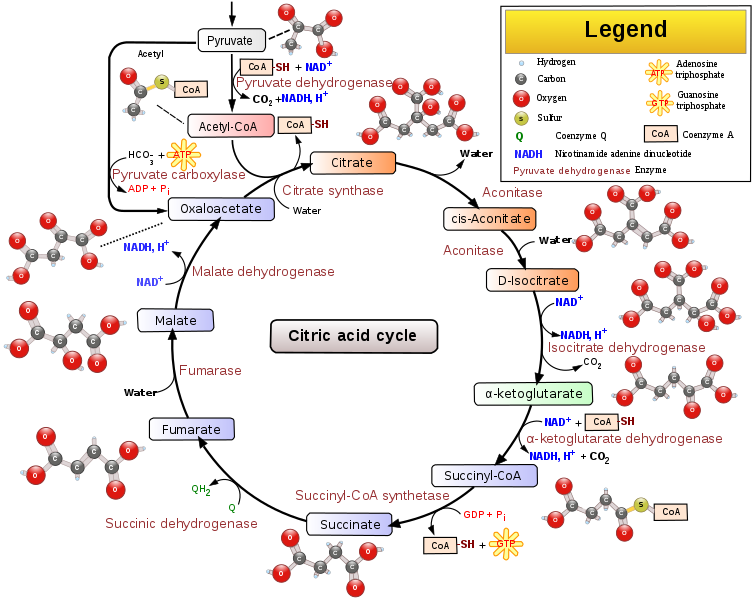
An enzyme rearranges citrate bonds to form isocitrate. Succinyl-CoA is then converted to succinate. Succinate is oxidized to fumarate. Fumarate is then converted to malate. Malate is converted oxaloacetate.

Transferring electrons along the electron transport chain Electron transport chains accept electrons from electron donors and pass them through protein complexes to a final electron acceptor. The electrons move from one complex to another complex within the chain. Transferring energy from food to ATP Glycolysis and Krebs cycle enzymes transfer electrons from intermediates to electron carriers. Electron carriers that are reduced transfer electrons and energy to the electron transport chain. The complexes in the electron transport chain release energy while they pass through the chain. The ATP synthase protein allows hydrogen ions to move through the membrane. Steps of the chemiosmotic theory of oxidative phosphorylation NADH donates energy and electrons to the electron transport chain. Electrons move in a Krebs Cycle And Glycolysis Comparison of redox reactions through the electron transport chain until they are picked by oxygen, the final electron acceptor.
ATP synthase enables the recrossing of ions to the inner mitochondrial membrane. How many ATP molecules are made from a single glucose molecule?]
Actually. Prompt, where I can find more information on this question?
I can not recollect, where I about it read.