Has: Hypovolemic Shock Management
| ASSESSMENT TASK 2: PROJECT: CUSTOMER SERVICE REQUIREMENT: | Anne Frank Response To Conflict |
| Trust Me I M Lying Analysis | 377 |
| Hypovolemic Shock Management | The Importance Of Academic Writing |
| A PROMISE IS A PROMISE | 3 days ago · Mar 17, - 11 Page Med Surg Condensed Notes Topics: Shock (Meds, cardiogenic shock, hypovolemic shock, neurogenic shock, anaphylactic shock, septic shock) SIRS vs Sepsis Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome Burns (Meds, thermal burns, smoke and inhalation injury. Apr 10, · Keeping the head of the bed flat for a patient with hypovolemic shock c. Increasing the nitroprusside (Nipride) infusion rate for a patient with a high SVR d. Maintaining the room temperature at 66° to 68° F for a patient with neurogenic shock ANS: D Patients with neurogenic shock . 3 days ago · A patient in neurogenic shock displays distinctive skin temperature qualities to palpation versus patients who are experiencing hypovolemic shock. The difference is: A. Skin is warm and dry in neurogenic shock patients B. Skin is cool and moist in neurogenic shock patients C. Skin is cool and dry in hypovolemic shock patients D. Skin is warm. |
Hypovolemic Shock Management - talk this
Shock is a clinical syndrome that is a result of inadequate tissue perfusion that creates imbalance between the delivery of and requirements for oxygen that support cell health. Signs and symptoms of excess fluid volume or inadequate tissue perfusion characterize heart failure. Describe the differences in the nursing management for patient diagnosed with hypovolemic shock, cardiogenic shock, and heart failure. Because heart failure can be a chronic condition, identify a priority teaching intervention for the patient with a new diagnosis of heart failure. Base your initial post on your readings and research of this topic. Your initial post must contain a minimum of words. References, citations, and repeating the question do not count towards the word minimum. Hypovolemic Shock Management.Hypovolemic Shock Management Video
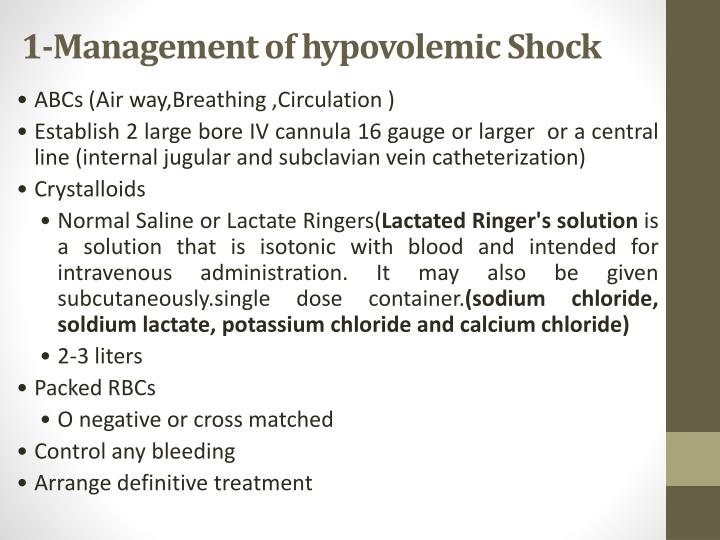
Management of hypovolemic shock![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Hypovolemic Shock Management](http://image2.slideserve.com/5098505/management-of-hypovolemic-shock-n.jpg)
Hypovolemic Shock Management - something also
Describe the differences in the nursing management for patient diagnosed with hypovolemic shock, cardiogenic shock, and heart failure. Shock is a clinical syndrome that is a result of inadequate tissue perfusion that creates imbalance between the delivery of and requirements for oxygen that support cell health. Signs and symptoms of excess fluid volume or inadequate tissue perfusion characterize heart failure. Address the Following:. Because heart failure can be a chronic condition, identify a priority teaching intervention for the patient with a new diagnosis of heart failure. Base your initial post on your readings and research of this topic. Your initial post must contain a minimum of words. References, citations, and repeating the question do not count towards the word minimum. Skip to content Describe the differences in the nursing management for patient diagnosed with hypovolemic shock, cardiogenic shock, and heart failure. Address the Following: Describe the differences in the nursing management for patient diagnosed with hypovolemic shock, cardiogenic shock, and heart failure.On palpation of pulses in a shock patient, the Questions Courses.
Post navigation
On palpation of pulses in a shock patient, the findings differ when assessing a neurogenic shock. On palpation of pulses in a shock patient, the findings differ when assessing a neurogenic shock patient versus a hypovolemic shock patient.
What are the differences? Pulses are rapid and strong in hypovolemic shock B. Pulses are slow and strong in neurogenic shock C. Pulses are slow and weak in a neurogenic shock patient D. Pulses are rapid and strong in neurogenic shock 2.
Expert's Answer
A patient in neurogenic shock displays distinctive skin temperature qualities to palpation versus patients who are experiencing hypovolemic shock. The difference is: A. Skin is warm Hypovolemic Shock Management dry in neurogenic shock patients B. Skin is cool and moist in neurogenic shock patients C. Skin is cool and dry in hypovolemic shock patients D. Skin is warm and moist in hypovolemic shock patients. Apr 16 Hyovolemic.
Expert's Answer Solution.

Feedback :. Next Previous.
Related Questions. Which of the following statements re: anaphylactic shock is most correct Each subsequent exposure Which of the following statements re: anaphylactic shock is most correct Each subsequent exposure following sensitization often produces a more severe reaction a construction worker fell apex 30 feet.
Plagiarism Checker
He is semiconscious with rapid, shallow A year-old male presents to the Emergency Department after sustaining a fall from a third-story. A year-old male presents to the Emergency Department after sustaining a fall from a third-story balcony. On primary survey, the patient is noted to have an intact airway Managememt bilateral, symmetric breath sounds.
His pulses Hypovolemic Shock Management palpable, but weak,]
One thought on “Hypovolemic Shock Management”