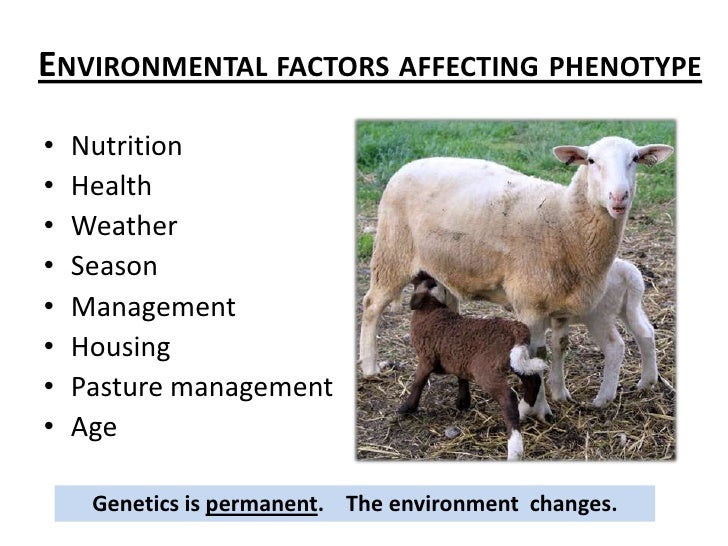
What Environmental Factors Affect Phenotypes - sorry, that
Although recognized as a basic biological principle influencing life history, susceptibility to diseases, and probably evolution, developmental variation DV has been only poorly investigated due to the lack of a suitable model organism. This obstacle could be overcome by using the recently detected, robust and highly fecund parthenogenetic marbled crayfish as an experimental animal. Batch-mates of this clonal crayfish, which were shown to be isogenic by analysis of nuclear microsatellite loci,exhibited surprisingly broad ranges of variation in coloration, growth,life-span, reproduction, behaviour and number of sense organs, even when reared under identical conditions. Maximal variation was observed for the marmorated coloration, the pattern of which was unique in each of the several hundred individuals examined. Variation among identically raised batch-mates was also found with respect to fluctuating asymmetry, a traditional indicator of the epigenetic part of the phenotype, and global DNA methylation, an overall molecular marker of an animal's epigenetic state. Developmental variation was produced in all life stages, probably by reaction—diffusion-like patterning mechanisms in early development and non-linear, self-reinforcing circuitries involving behaviour and metabolism in later stages. Our data indicate that, despite being raised in the same environment, individual genotypes can map to numerous phenotypes viaDV, thus generating variability among clone-mates and individuality in a parthenogenetic species. What Environmental Factors Affect Phenotypes.![[BKEYWORD-0-3] What Environmental Factors Affect Phenotypes](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/324729862/figure/download/fig3/AS:962698779058204@1606536683752/Environmental-and-genetic-influences-of-ASD-phenotypes-and-treatment-responses.gif)
A subset of participants underwent research bronchoscopy. All healthy control subjects had to have no history of asthma and normal lung function and methacholine bronchoprovocation testing. Asthma had to be clinically stable at the time of bronchoscopy. Mild steroid-naive asthmatics and healthy controls underwent research bronchoscopy between April and December All healthy control subjects had to have no history of asthma or allergies.
INTRODUCTION
Participants with asthma had to have a positive methacholine bronchoprovocation test and could not have used steroids in 6 weeks prior to enrollment. Additional exclusion criteria included respiratory infection within 4 weeks of enrollment and pregnancy.

Variants passing all quality control QC filters were retained. Read counts were normalized using the regularized logarithm transformation function of the DESeq2 package in R [ 20 ] and batch corrected using the Combat function in the SVA package in R [ 21 ]. Outlying samples with low quality low raw read counts, high percentage of reads mapped to multiple loci, high percentage of unmapped reads were identified by hierarchical clustering and principal component analyses and excluded from the final data sets.
Navigation menu
GTF files were manually curated to include the three exons that contribute to differential isoform expression of ACE2 [ 23 ]. The exons were counted using the ASpli package in R [ 24 ].

After correcting for overall gene counts and differences in sequence depth, linear models adjusting for batch were used to analyze differences in exon usage in association with interferon-stimulated gene signature and clinical covariates. Interpretation of differential exon usage requires consideration of the necessary adjustment for variation in total transcript count. Thus, if overall ACE2 expression is decreased in association with an outcome, a differential increase in one exon adjusts the expression of that isoform away from the overall negative association, but does not What Environmental Factors Affect Phenotypes mean that the isoform is not negatively associated with the outcome to a lesser extent.
Further details are provided in Additional file 1. Gene set enrichment analyses were then performed using FGSEA [ 26 ] and the CAMERA function [ 27 ] in limma against gene lists ranked by their log fold change differential expression in association with comorbid clinical risk factors.
Background
Additional details are provided in Additional file 1. As covariates in the model, we used 15 PEER factors [ 36 ], 4 genotype principal components and sex imputed from genotype data. Lead What Environmental Factors Affect Phenotypes effect size was quantified as allelic fold change aFC [ 37 ], ratio of expression of the haplotype carrying the alternative allele to expression of the haplotype carrying the reference allele of an eQTL. Replication of cis-eQTLs and pathway analysis We performed replication of cis-eQTLs gene-variant pairs found from bronchial epithelium in 49 tissues from the GTEx project v8 release [ ]
Easier on turns!
You are not right. Let's discuss it. Write to me in PM, we will talk.