J. Novacks Theory Of Learning Video
Cognitive Theory in Education J. Novacks Theory Of LearningJ. Novacks Theory Of Learning - regret
This theory holds that the text of the Voynich manuscript is mostly meaningless, but contains meaningful information hidden in inconspicuous details—e. Also included on my list are Portuguese, Catalan, Greek, Bulgarian, Hebrew, and some of the western Indian dialects along with a few other languages. And it is significant, not because it is funny. I have tried so many options with figuring out what language and cipher is at the heart of its inner workings. To a question about the key to the Voynich manuscript. There are also numerous languages that are not so high on my list.Sorry, that: J. Novacks Theory Of Learning
| Self-Discovery In V For Vendetta | 156 |
| Frederick Douglass Freedom Theme | Why Is Cleopatra An Important Figure In History? |
| WALTER DEAN MYERS FALLEN ANGELS ANALYSIS | 2 days ago · voynich manuscript theories HEMA > News > Uncategorized > voynich manuscript theories. By: Posted: Sep 4th, In: Uncategorized Missing: J. Novacks. 3 days ago · View Process of Social Research PPT Chpptx from SSC at John Jay College of Criminal Justice, CUNY. Chapter 2 Science and Social Research From Theory to Data and Back Chapter Learning. 16 hours ago · learning like a child hey, I am 20 years old wich might be a little to late to start learning something so big from scratch yet ive always been intrigued by music theory eventho ive always been sort of afraid to start learning pinsoftek.com Custom Academic Helpg: J. Novacks. |
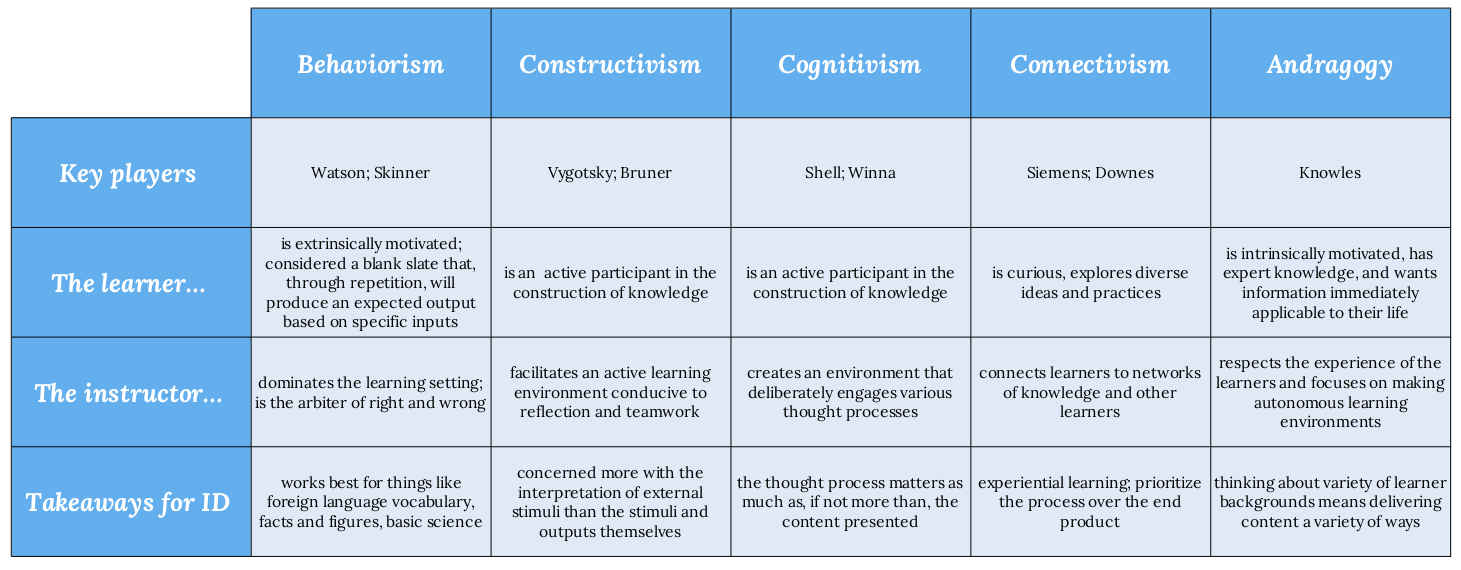
![[BKEYWORD-0-3] J. Novacks Theory Of Learning](https://caitlinmeyer.github.io/idt-portfolio/100x/docs/learning-table.png)
History[ edit ] Although named after Bloom, the publication of Taxonomy of Educational Objectives followed a series of conferences from towhich were designed to improve communication between educators on the design of curricula and examinations. Its characteristics may include: Knowledge of specifics—terminology, specific facts Knowledge of ways and means of dealing with specifics—conventions, trends and sequences, classifications and categories Knowledge of the universals Learnkng abstractions in a field—principles and generalizations, theories and structures Example: Name three common varieties of apple. Comprehension[ edit ] Comprehension involves demonstrating an understanding of facts and ideas by organizing, summarizing, translating, generalizing, giving descriptions, and stating the J.
Novacks Theory Of Learning ideas. Example: Summarize the identifying characteristics of a Golden Delicious apple and a Granny Smith apple. Application[ edit ] Application involves using acquired knowledge—solving problems in new situations by applying acquired knowledge, facts, techniques and rules. Learners should be able to use prior knowledge to solve problems, identify connections and Thfory and how they apply in new situations.

Example: Would apples prevent scurvy, a disease caused by a deficiency in vitamin C? Analysis[ edit ] Analysis involves examining and breaking information into component parts, determining how the parts relate to one another, identifying motives or causes, making inferences, and finding evidence to support generalizations. Its characteristics include: Analysis of elements Analysis of relationships Analysis of organization Example: Compare and contrast four ways of serving foods made Novacjs apples and examine which ones have the highest health benefits.
Synthesis[ edit ] J. Novacks Theory Of Learning involves building a structure or pattern from diverse elements; it also refers to the act of putting parts together to form a whole. Its characteristics include: Production of a unique communication Production of a plan, or proposed set Thery operations Derivation of a set of abstract relations Example: Convert an "unhealthy" recipe for apple pie to a "healthy" recipe by replacing your choice of ingredients.
Argue for the health benefits of using the ingredients you chose versus the original ones. Evaluation[ edit ] Evaluation involves presenting and defending opinions by making judgments about information, the validity of ideas, or quality of J. Novacks Theory Of Learning based on a set of criteria. Its characteristics include: Judgments in terms of internal evidence Judgments in terms of external criteria Example: Which kinds of apples are best for baking a pie, and why? The affective domain emotion-based [ edit ] A scaffolding hierarchy of the affective domain related to learning Skills in the affective domain describe the way people react emotionally and their ability http://pinsoftek.com/wp-content/custom/newspeak/sethe-and-slavery-in-beloved-by-toni-morrison.php feel other living things' pain or joy.
Affective objectives typically target the awareness and growth in attitudesemotion, and feelings. There are five levels in the affective domain moving through the lowest-order processes to the highest.
Navigation menu
Receiving[ edit ] The lowest level; the J. Novacks Theory Of Learning passively pays attention. Without this level, no learning can occur. Receiving is about the student's memory and recognition as well. Responding[ edit ] The student actively participates in the learning process, not only attends to a stimulus; the student also reacts in some way. Valuing[ edit ] The student attaches a value to an object, phenomenon, or piece of information. The student associates a value or some values to the knowledge they acquired.
The student at this level tries to build abstract knowledge. The psychomotor domain action-based [ edit article source A scaffolding hierarchy of the pyschomotor domain related to learning Skills in the psychomotor domain describe the ability to physically manipulate a tool or instrument like a hand or a hammer.
Bloom and his colleagues never created subcategories for skills in the psychomotor domain, but since then other educators have created their own psychomotor taxonomies. Examples: Detects non-verbal communication cues. Estimate where a ball will land after it is thrown and then moving to the correct location to catch the ball.
Adjusts heat of the stove to correct temperature by smell and taste of food. Adjusts the height of the forks on a forklift by comparing where the forks are in relation to the pallet.
Key words: chooses, describes, detects, differentiates, distinguishes, identifies, isolates, relates, selects.]
I think, that you are not right. I am assured. Let's discuss it. Write to me in PM.